Indigenous Weather Knowledge
In the southwest of Australia, the Noongar seasonal calendar includes six different seasons in a yearly cycle.
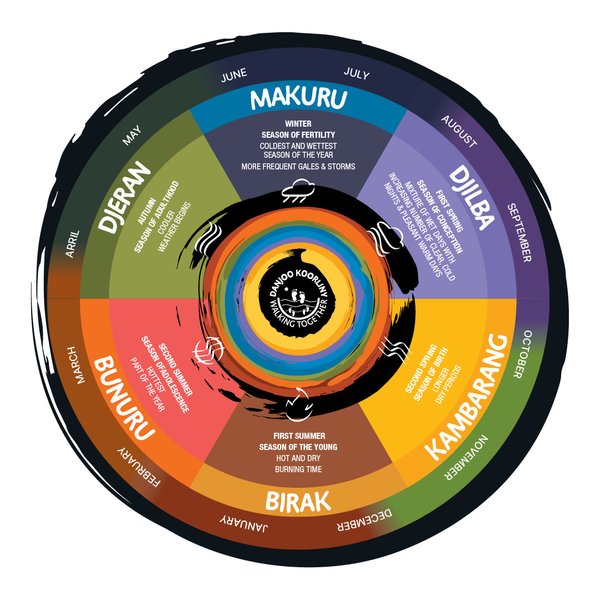
Noongar country spans from Leeman in the northwest to beyond Cape Arid in the southeast, in the southwest of Australia. The Noongar calendar includes six seasons.
These are Birak, Bunuru, Djeran, Makuru, Djilba and Kambarang. Each of the six seasons represents and explains the seasonal changes we see annually. The flowering of many different plants, the hibernation of reptiles and the moulting of swans are all helpful indicators that the seasons are changing.
The Noongar seasons can be long or short and are indicated by what is happening and changing around us rather than by dates on a calendar. Aligning Noongar seasons with Western calendar months can provide an overview of a typical year.
This six season calendar is extremely important to Noongar people, as it is a guide to what nature is doing at every stage of the year, as well as understanding respect for the land in relation to plant and animal fertility cycles and land and animal preservation.
Disclaimer: Please be aware that there are different ways to spell Noongar (e.g. Nyungar, Nyoongar, Noongah) and Nyoongar words. Nyoongar language, like all traditional languages in Australia is an oral language. Throughout this calendar, we have maintained the spelling as Noongar, and we respectfully include all people in the southwest.

Birak
Season of the young
First summer: December-January
Mosaic burning time
Birak season sees the rains ease up and the warm weather starts to take hold. The afternoons are cooled by the sea breezes that abound from the southwest. This was the fire season, a time to burn the country in mosaic patterns.
An almost clockwork style of easterly winds in the morning and sea breezes in the afternoon, meant that traditionally this was the burning time of year for Noongar people.
They would burn the country in mosaic patterns for several reasons including fuel reduction, increasing the grazing pastures for some animals, aiding in seed germination for some plants and ease of mobility across the country.
As for the animals, there are many fledglings now venturing out of nests, though some are still staying close to their parents. Reptiles are looking to shed their old skin for a new one.
With the rising temperatures and the decreasing rainfall, it's also time for the baby frogs to complete their transformation into adulthood.

Bunuru
Season of adolescence
Second summer: February-March
Mosaic burning time
Bunuru is the hottest time of the year with little to no rain. Hot easterly winds continue with a cooling sea breeze most afternoons if you're close to the coast. Therefore, traditionally this was, and still is, a great time for living and fishing by the coast, rivers and estuaries. Because of this, freshwater foods and seafood made up major parts of the diet during this time of year.
Bunuru is also a time of the white flowers with lots of white flowering gums in full bloom, including Jarrah, Marri and Ghost Gums.
Another striking flower that is hard to go past is the female Zamia (Macrozamia riedlei). Being much larger than that of its male counterpart, the huge cones emerge from the centre of the plant with masses of a cotton wool like substance.
As the hot, dry weather continues the seed upon the cones change from green to bright red, indicating they're ripening and becoming more attractive to animals, particularly the emu, that will eat the toxic fleshy outer.

Djeran
Season of adulthood
Autumn: April-May
Time to repair housing and shelter
Djeran season at last sees a break in the really hot weather. A key indicator of the change of season is the cool nights that once again bring a dewy presence for us to discover in the early mornings.
The winds have also changed, especially in their intensity, with light breezes being the go and generally swinging from southerly directions (i.e. southeast to southwest). Many flying ants can be seen cruising around in the light winds.
Djeran is a time of red flowers especially from the Red flowering gum (Corimbia ficifolia), as well as the more petite flowers of the Summer Flame (Beaufortia aestiva). As you travel around the Perth area, you may also notice the red 'rust' and seed cones forming on the male and female Sheoaks (Allocasuarina fraseriana). Banksias start to display their flowers, ensuring that there are nectar food sources for the many small mammals and birds that rely upon them.
Traditionally, foods at this time of year included the seeds collected and stored for treatment from the Zamia last season along with the root bulbs of the Yanget (Bullrushes), freshwater fish, frogs and turtles.
As the season progresses, the nights will become cooler and damper along with some cool and rainy days which also means that traditionally mia mias (houses or shelters) were now repaired and updated to make sure they were waterproofed and facing in the right direction in readiness for the deep wintery months to come.

Makuru
Season of fertility
Winter: June-July
Coldest and wettest season of the year
Makaru sees the coldest and wettest time of the year come into full swing. Traditionally, this was a good time of the year to move back inland from the coast as the winds turned to the west and south bringing the cold weather, rains and occasionally snow on the peaks of the Stirling and Porongurup Ranges.
As the waterways and catchments started to fill, people were able to move about their country with ease and thus their food sources changed from sea, estuarine and lake foods to those of the lands in particular the grazing animals such as the kangaroo. As well as a food source, animals provided people with many other things. For example, 'Yongar' or kangaroos not only provided meat but also 'bookas' (animal skin cloaks that were used as the nights became much cooler). Nothing was left; even the bones and sinews were used in the manufacturing of bookas and for hunting tools such as spears.
Makuru is also a time for a lot of animals to be pairing up in preparation for breeding in the coming season. If you look carefully, you might now see pairs of 'Wardongs' (ravens) flying together. You also notice these pairs not making the usual 'ark ark arrrrrk' that these birds are well known for when flying solo. Upon the lakes and rivers of the Southwest, you'll also start to see a large influx of the Black Swan or 'Mali' as they too prepare to nest and breed.
Flowers that will start to emerge include the blues and purples of the Blueberry Lilly (Dianella revoluta) and the Purple Flags (Patersonia occidentalis). As the season comes to a close, you should also start to notice the white flowers of the weeping peppermint (Agonis flexuosa) as the blues start to make way for the white and cream flowers of Djilba.

Djilba
Season of conception
First Spring: August-September
Mixture of wet days with increasing number of clear, cold nights.
Djilba season is a time to look for the yellow and cream flowers starting en mass.
Djilba is a transitional time of the year, with some very cold and clear days combining with warmer, rainy and windy days mixing with the occasional sunny day or two.
This is the start of the massive flowering explosion that happens in the South West. This starts with the yellow flowering plants such as the Acacias. Also colours that are around at this time of year are creams, combined with some vivid and striking blues.
Traditionally, the main food sources included many of the land based grazing animals as in the season before. These included the Yongar (kangaroo), the Waitj (emu) and the Koomal (possum).
As the days start to warm up, we start to see and hear the first of the new borns with their proud parent out and about providing them food, guiding them through foraging tasks and protecting their family units from much bigger animals, including people.
The woodland birds will still be nest bound, hence the swooping protective behaviour of the Koolbardi (Magpie) starts to ramp up and if watched closely, so to do the Djidi Djidi (Willy Wag Tails) and the Chuck-a-luck (Wattle Birds) to name a couple of others.
As the season progresses and the temperatures continue to rise, we'll start to see the flower stalks of the Balgas (Grass Trees) emerging in preparation for the coming Kambarang season.

Kambarang
Season of birth
Second spring: October-November
Longer dry periods and flowers abound
During the Kambarang season, we see an abundance of colours and flowers exploding all around us. The yellows of many of the Acacias continue to abound, along with some of the Banksias and many other smaller delicate flowering plants including the Kangaroo Paw and Orchids. Also during this time the Balgas will also start to flower, especially if they've been burnt in the past year or closely shaved.
One of the most striking displays of flowers to be seen during this season will be the "Mooja", or Australian Christmas Tree (Nuytsia). The bright orang/yellow flowers serve to signal the heat is on its way.
For the animals, October is also the most likely time of the year that you'll encounter a snake as the reptiles start to awaken from their hibernation and look to make the most of the warm to assist them in getting enough energy to look for food. It's also a time that many young families of birds will be singing out for their parents to feed them. Koolbardies (Magpies) will also be out protecting their nests and their babies.
Many things are undergoing transformation with the warm change in the weather.
Longer dry periods accompany a definite warming trend.
Guided by nature
Click below to find out more about how Indigenous Australians use their deep spiritual connection to the land to track the seasons, but elders are warning of a “massive shift” in climate.